
For a gas that is a mixture of two or more pure gases, the gas composition must be known before compressibility can be calculated. Compressibility factor values are usually obtained by calculation from equations of state (EOS), such as the virial equation which take compound-specific empirical constants as input. In general, deviation from ideal behaviour becomes more significant the closer a gas is to a phase change, the lower the temperature or the larger the pressure. It is a useful thermodynamic property for modifying the ideal gas law to account for the real gas behaviour.

It is simply defined as the ratio of the molar volume of a gas to the molar volume of an ideal gas at the same temperature and pressure. In thermodynamics, the compressibility factor ( Z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, is a correction factor which describes the deviation of a real gas from ideal gas behaviour. Read this K-value off the chart (approximately 21.3).
DePriester in an article in Chemical Engineering Progress in 1953.

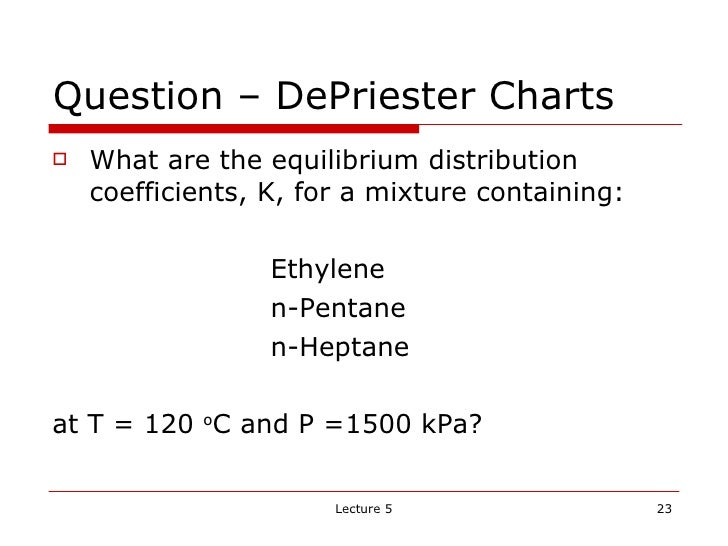
( December 2018)ĭePriester Charts provide an efficient method to find the vapor-liquid equilibrium ratios for different substances at different conditions of pressure and temperature. Please introduce links to this page from related articles try the Find link tool for suggestions. This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
